Understanding Fatty Liver: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
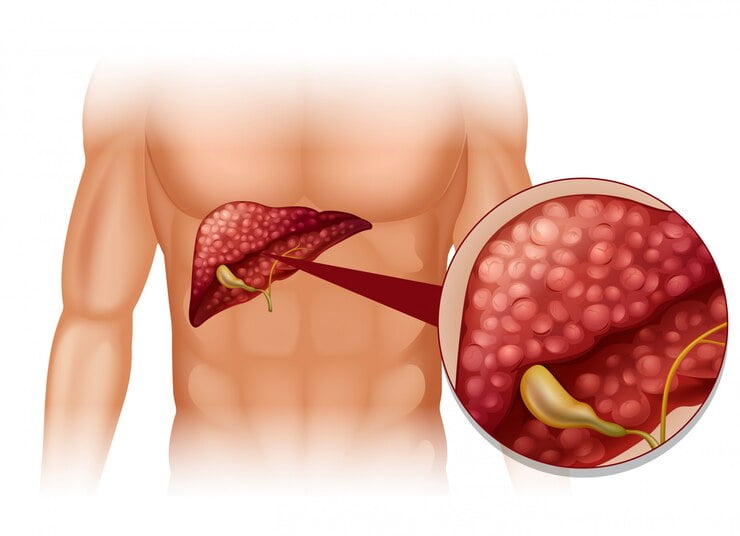
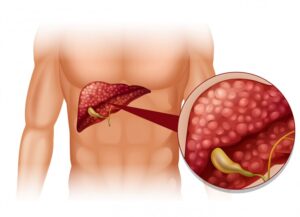
The liver, often referred to as the body’s detox powerhouse, plays a crucial role in processing nutrients, filtering toxins, and regulating metabolism. However, when fat accumulates in the liver cells excessively, it can lead to a condition known as fatty liver disease. This condition, which affects millions of people worldwide, can have serious implications for overall health if left untreated. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for fatty liver disease.
What Causes Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver disease can be broadly classified into two types: alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
1. *Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):* As the name suggests, AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Chronic alcohol abuse can overwhelm the liver’s ability to metabolize fat, leading to the accumulation of fat in liver cells.
2. *Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):* NAFLD is more common and is not associated with alcohol consumption. Instead, it is closely linked to factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. Lifestyle factors, such as a poor diet and sedentary behavior, can contribute to the development of NAFLD.
Recognizing the Symptoms
In its early stages, fatty liver disease may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience:
– Fatigue
– Weakness
– Abdominal discomfort or pain
– Swelling in the abdomen
– Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
– Elevated liver enzymes (detected through blood tests)
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the disease and the presence of any complications.
Managing Fatty Liver Disease
While there is no specific medication to treat fatty liver disease, lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of management. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. *Healthy Diet:* Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support liver health. Limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats is crucial.
2. *Regular Exercise:* Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
3.*Weight Management:* Losing excess weight, if overweight or obese, can significantly improve liver health. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can lead to significant reductions in liver fat and improve liver function.
4. *Limit Alcohol Consumption:* If diagnosed with fatty liver disease, it’s essential to reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption to prevent further liver damage.
5. *Monitor Health:* Regular medical check-ups and monitoring of liver function tests are essential for detecting any changes in liver health and addressing them promptly.
Seeking Medical Guidance
If you suspect you may have fatty liver disease or are experiencing symptoms related to liver dysfunction, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. Your doctor can perform diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, or liver biopsy, to confirm the diagnosis and recommend appropriate management strategies.
In conclusion, fatty liver disease is a common yet potentially serious condition that requires attention and proactive management. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management, individuals can support liver health and reduce the risk of complications associated with fatty liver disease. Remember, small changes can make a big difference in promoting liver health and overall well-being.
Recent Posts


Exploring the Benefits of Chicken Salad